SAB1401533
Monoclonal Anti-SIX2 antibody produced in mouse
clone 1G11, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(2)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
1G11, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
species reactivity
human
technique(s)
capture ELISA: suitable
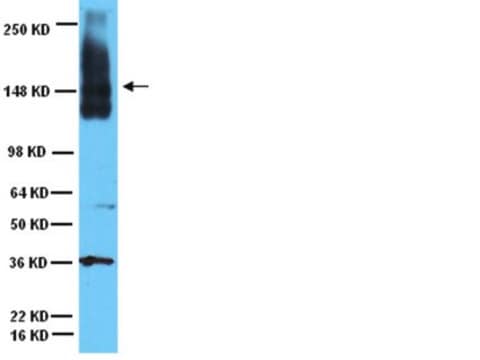
western blot: 1-5 μg/mL
isotype
IgG1κ
General description
This gene is a member of the vertebrate gene family which encode proteins homologous to the Drosophila ′sine oculis′ homeobox protein. The encoded protein is a transcription factor which, like other members of this gene family, may be involved in limb or eye development. (provided by RefSeq)
Immunogen
SIX2 (AAH24033, 1 a.a. ~ 291 a.a) full-length recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa.
Sequence
MSMLPTFGFTQEQVACVCEVLQQGGNIERLGRFLWSLPACEHLHKNESVLKAKAVVAFHRGNFRELYKILESHQFSPHNHAKLQQLWLKAHYIEAEKLRGRPLGAVGKYRVRRKFPLPRSIWDGEETSYCFKEKSRSVLREWYAHNPYPSPREKRELTEATGLTTTQVSNWFKNRRQRDRAAEAKERENNENSNSNSHNPLNGSGKSVLGSSEDEKTPSGTPDHSSSSPALLLSPPPPGLPSLHSLGHPPGPSAVPVPVPGGGGADPLQHHHGLQDSILNPMSANLVDLGS
Sequence
MSMLPTFGFTQEQVACVCEVLQQGGNIERLGRFLWSLPACEHLHKNESVLKAKAVVAFHRGNFRELYKILESHQFSPHNHAKLQQLWLKAHYIEAEKLRGRPLGAVGKYRVRRKFPLPRSIWDGEETSYCFKEKSRSVLREWYAHNPYPSPREKRELTEATGLTTTQVSNWFKNRRQRDRAAEAKERENNENSNSNSHNPLNGSGKSVLGSSEDEKTPSGTPDHSSSSPALLLSPPPPGLPSLHSLGHPPGPSAVPVPVPGGGGADPLQHHHGLQDSILNPMSANLVDLGS
Biochem/physiol Actions
SIX2 (SIX homeobox 2) is responsible for the regulation of cartilage growth and differentiation in endochondral skeleton. SIX2 also participates in the craniofacial skeletal muscle formation. It might prevent the abnormal drooping eyelids, by weakening the ability of levator muscle to contract. SIX2 haploinsufficiency is linked with congenital ossicle malformation. Mutation in SIX2 is found to be associated with the development of urinary tract, kidney, anterior cranial base, limb tendon and the formation of pyloric sphincter. Deletion in the gene might cause autosomal dominant frontonasal dysplasia syndrome. Mutation in the gene leads to renal hypodysplasia and also chemotherapy-resistant blastemas.
Physical form
Solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class
10 - Combustible liquids
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Robert B Hufnagel et al.
American journal of medical genetics. Part A, 170A(2), 487-491 (2015-11-20)
The frontonasal dysplasias are a group of craniofacial phenotypes characterized by hypertelorism, nasal clefting, frontal bossing, and abnormal hairline. These conditions are caused by recessive mutations in members of the aristaless gene family, resulting in abnormal cranial neural crest migration
Jing Guan et al.
Journal of human genetics, 61(11), 917-922 (2016-07-08)
The ossicles represent one of the most fundamental morphological features in evolutionary biology of the mammalians. The mobile ossicular morphology abnormalities result in the severe conductive hearing loss. Development and patterning of the middle ear malformation depend on genetic and
A new frontonasal dysplasia syndrome associated with deletion of the SIX2 gene.
Hufnagel RB
American Journal of Medical Genetics, 170A(2), 487-491 (2016)
SIX2 haploinsufficiency causes conductive hearing loss with ptosis in humans.
Guan J
Journal of Human Genetics, 61(11), 917-922 (2016)
Differential regulation of mouse and human nephron progenitors by the Six family of transcriptional regulators.
O'Brien LL
Development, 143(4), 595-608 (2016)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service