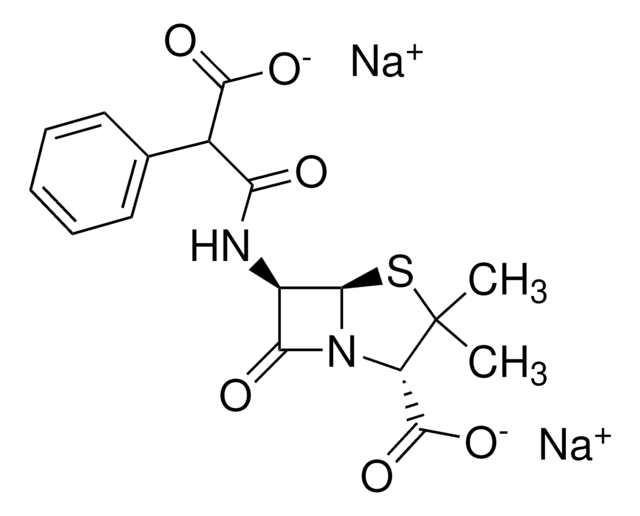
C1389
Carbenicillin disodium salt
89.0-100.5% anhydrous basis
동의어(들):
Carbenicillin, Disodium carbenicillin, α-Carboxybenzylpenicillin disodium salt
About This Item
추천 제품
생물학적 소스
synthetic (chemical)
Quality Level
분석
89.0-100.5% anhydrous basis
양식
powder
색상
white to off-white
solubility
H2O: 50 mg/mL
항생제 활성 스펙트럼
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
동작 모드
cell wall synthesis | interferes
저장 온도
2-8°C
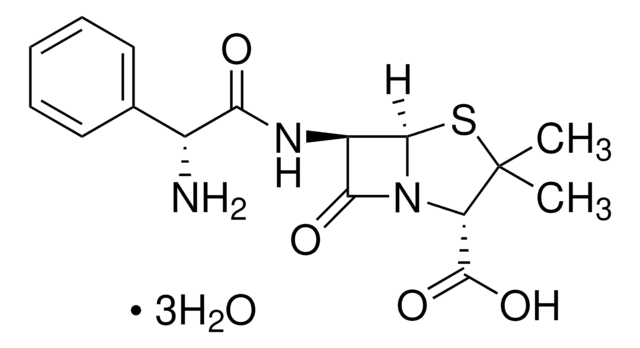
SMILES string
[Na+].[Na+].CC1(C)S[C@@H]2[C@H](NC(=O)C(C([O-])=O)c3ccccc3)C(=O)N2[C@H]1C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C17H18N2O6S.2Na/c1-17(2)11(16(24)25)19-13(21)10(14(19)26-17)18-12(20)9(15(22)23)8-6-4-3-5-7-8;;/h3-7,9-11,14H,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)(H,24,25);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t9?,10-,11+,14-;;/m1../s1
InChI key
RTYJTGSCYUUYAL-YCAHSCEMSA-L
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
일반 설명
Carbenicillin is commonly used in cell biology applications to prevent the growth of bacterial contaminants. It is also used in microbiology to select for bacteria that have been transformed with a vector harboring the gene encoding beta-lactamase, which makes them resistant to carbenicillin.
애플리케이션
- in the preparation of Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plates and media
- as a selective agent in the culture media to prevent the growth of bacterial contaminants
- in a study focused on the development of monoclonal antibodies
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Antimicrobial spectrum: Active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
특징 및 장점
- Broad-spectrum antibiotic with bactericidal and beta-lactamase resistant activity
- Effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Commonly used in Cell Biology and Biochemical applications
- Offers greater stablility than ampicillin
저장 및 안정성
분석 메모
기타 정보
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
이미 열람한 고객
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.