1242000
USP
Erythromycin
United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
pharmaceutical primary standard
Famille d'API
erythromycin
Forme
solid
Fabricant/nom de marque
USP
Application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
Format
neat
Température de stockage
−20°C
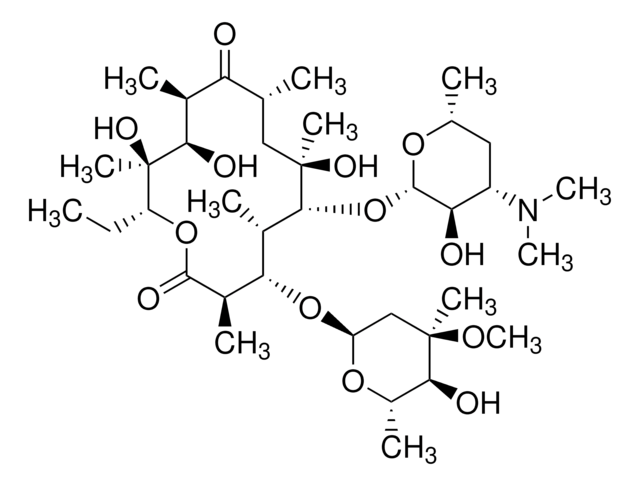
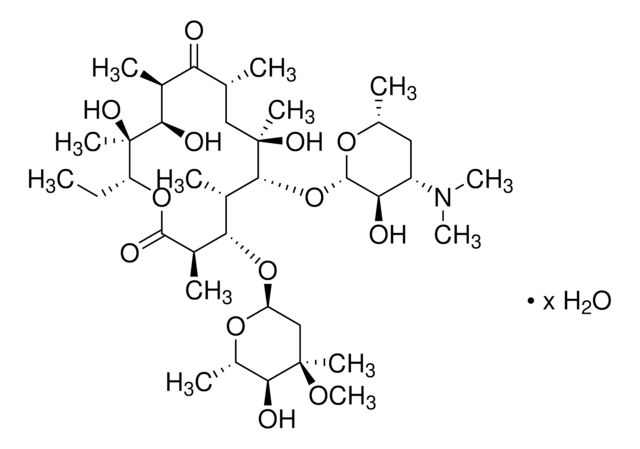
Chaîne SMILES
CC[C@H]1OC(=O)[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@H]2C[C@@](C)(OC)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O2)[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@@H]3O[C@H](C)C[C@@H]([C@H]3O)N(C)C)[C@](C)(O)C[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@]1(C)O
InChI
1S/C37H67NO13/c1-14-25-37(10,45)30(41)20(4)27(39)18(2)16-35(8,44)32(51-34-28(40)24(38(11)12)15-19(3)47-34)21(5)29(22(6)33(43)49-25)50-26-17-36(9,46-13)31(42)23(7)48-26/h18-26,28-32,34,40-42,44-45H,14-17H2,1-13H3/t18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,25-,26+,28-,29+,30-,31+,32-,34+,35-,36-,37-/m1/s1
Clé InChI
ULGZDMOVFRHVEP-RWJQBGPGSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by Saccharopolyspora erythraea, acting by inhibition of protein synthesis at the 50S ribosomal subunit. It is used to treat a variety of infections caused by susceptible organisms. The USP standard provides quality benchmarks for identification, assay, and dissolution studies in erythromycin formulations.
The USP biologics antibiotics category includes a wide range of antimicrobial agents that are essential in treating bacterial infections. These antibiotics are derived from various natural sources or synthesized to combat specific pathogens effectively. The USP provides comprehensive standards, reference materials, and analytical procedures to ensure the identity, quality, purity, and consistency of antibiotic therapeutics throughout their lifecycle.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) provides quality standards for biologics to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality throughout the manufacturing process. These standards assist manufacturers in adhering to regulatory requirements and help safeguard public health by reducing risks associated with biologics.
Application
- Erythromycin Stearate
- Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate
- Erythromycin Lactobionate for Injection
- Erythromycin Ointment
- Erythromycin Pledgets
- Erythromycin Injection
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Antimicrobial Spectrum: This product acts against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Attention
Notes préparatoires
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
Si vous avez besoin d'assistance, veuillez contacter Service Clients
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique