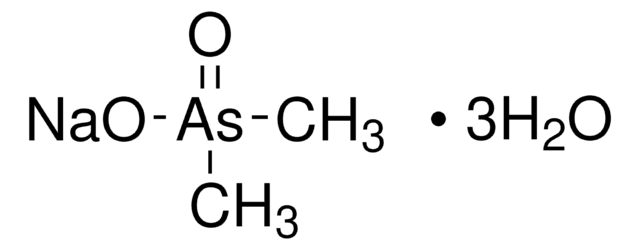97068
Sodium cacodylate Buffer
pH 6.5; 50 mM – Isopropanol 15% solution
Synonym(s):
Crystallization solution 8/Kit-No 18839
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352302
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Product Name
Sodium cacodylate Buffer pH 6.5; 50 mM – Isopropanol 15% solution,
form
liquid
Quality Level
final pH
6.5±0.2 ( in neat)
density
0.98 g/mL at 20 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
Related Categories
Application
Sodium cacodylate Buffer pH 6.5; 50 mM − Isopropanol 15% solution has been used:
- in washing the overnight fixed pancreas sections for transmission electron microscope assay
- in the preparation of fixation and post-fixation buffers and washing of cells for scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
- in diluting glutaraldehyde for the fixation of bacterial biofilm for SEM analysis
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 2 - Carc. 1B - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3
Storage Class
3 - Flammable liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
98.6 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
37.0 °C - closed cup
ppe
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Oral biofilm formation on different materials for dental implants
Silva TSO, et al.
Journal of Visualized Experiments, e57756-e57756 (2018)
Surgical retrieval, isolation and in vitro expansion of human anterior cruciate ligament-derived cells for tissue engineering applications
Gupta A, et al.
Journal of Visualized Experiments, e51597-e51597 (2014)
Emodin attenuated severe acute pancreatitis via the P2X ligand-gated ion channel 7/NOD-like receptor protein 3 signaling pathway
Zhang Q, et al.
Oncology Reports, 41(1), 270-278 (2019)
Trace Thome et al.
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology, 317(4), C701-C713 (2019-07-11)
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) leads to increased skeletal muscle fatigue, weakness, and atrophy. Previous work has implicated mitochondria within the skeletal muscle as a mediator of muscle dysfunction in CKD; however, the mechanisms underlying mitochondrial dysfunction in CKD are not
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service