M1254
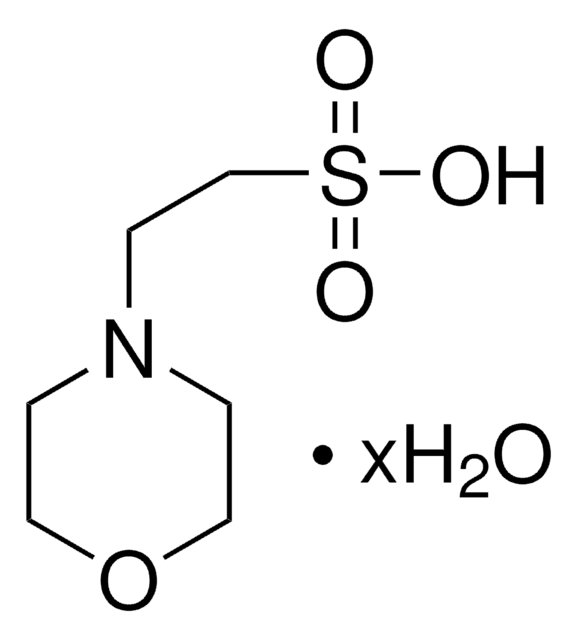
MOPS
≥99.5% (titration), crystalline powder
Synonym(s):
3-(N-Morpholino)propanesulfonic acid, 4-Morpholinepropanesulfonic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
MOPS, ≥99.5% (titration)
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.5% (titration)
form
crystalline powder
storage condition
dry at room temperature
technique(s)
affinity chromatography: suitable
electrophoresis: suitable
color
white
pH
2.5-4 (25 °C, 209 g/L)
useful pH range
6.5-7.9
pKa (25 °C)
7.2
solubility
water: 0.5 g/mL, clear, colorless
λ
33 % in H2O
suitability
suitable for HPLC
application(s)
clinical research
diagnostic assay manufacturing
life science and biopharma
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
OS(=O)(=O)CCCN1CCOCC1
InChI
1S/C7H15NO4S/c9-13(10,11)7-1-2-8-3-5-12-6-4-8/h1-7H2,(H,9,10,11)
InChI key
DVLFYONBTKHTER-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
MOPS serves various functions in diverse research domains. As a buffering agent, it can be used to stabilize pH in cell culture media, promoting optimal cell growth and function. Additionally, it may find application in protein purification in chromatography, stabilizes protein solutions, and acts as a reliable running buffer in various electrophoretic techniques, enabling efficient separation and analysis of biomolecules. MOPS also efficiently lyses cells for subsequent protein or nucleic acid extraction and stabilizes enzymes in solution, ensuring their activity for research purposes. It further proves valuable in fine-tuning the pH of growth media for optimal cell growth.
MOPS possesses additional advantages such as minimal interaction with metal ions especially with copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), cobalt (Co) ions, making it ideal for studies involving metal ions. It exhibits excellent water solubility, facilitating its use in various buffer formulations, and minimal lipid solubility, ensuring impermeability to membranes and minimizing interference with cellular processes. In summary, MOPS is a reliable buffer widely utilized across diverse biological disciplines, distinguished by its versatility, physiological relevance, minimal metal interaction, and ease of use, with its extensive applications in cell biology, protein studies, electrophoresis, and biochemical research.
Application
- a cell culture additive component in lentiviral particle production
- as a buffering agent in microbial growth medium and nuclei extraction buffer
- as a component of the MMSE-A buffer for isolating heart mitochondria
- as a component of the Synthetic Complete (SC) medium
- as a buffer in fluorescence quenching of NADH
Features and Benefits
- Ideal for Cell Biology and Biochemical research
- Can be used as a Buffer component for Electrophoresis and Protein separation
- Effective Buffering from pH 6.5-7.9 (25 °C) with a pKa of 7.2 (25 °C)
- Highly soluble in water
- Minimal metal ion binding
Packaging
- The current DRYPOUR®packaging configuration is in a 50L nestable drum
- 25KG-DP are the standard prepack offering
- Smaller volumes can be put in the same drum for variable configurations
- Improves operational efficiency by reducing material preparation time and increasing operator safety
- Minimizes caking of hygroscopic salts
- Offers triple protection: against moisture inside and outside, and against contamination
- This state-of-the-art design packaging system minimizes caking, thus significantly reducing the time needed for material preparation
- PE drum with our new tamper-evident seal, a polyethylene liner with integrated desiccant bags and a breathable interior Tyvek®liner
- Desiccant bags are firmly integrated into the polyethylene liner
- Triple protection delivers two invaluable results:
- Dramatically reduced caking
- No contamination risk from the desiccant
Other Notes
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
230.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
110 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service