31170
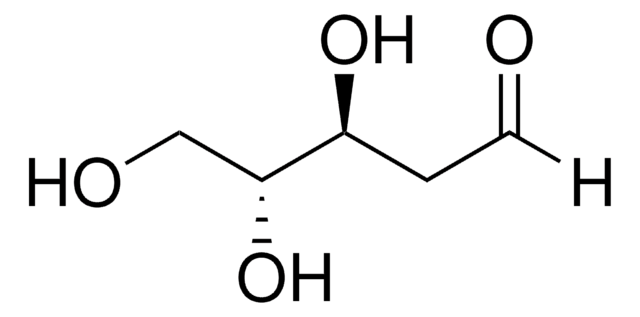
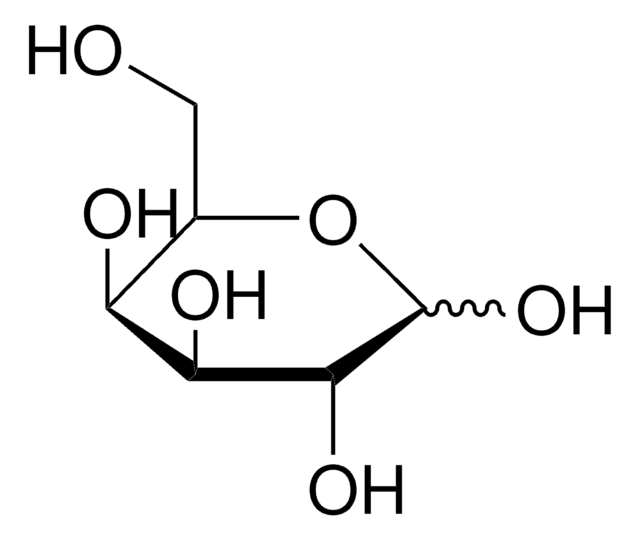
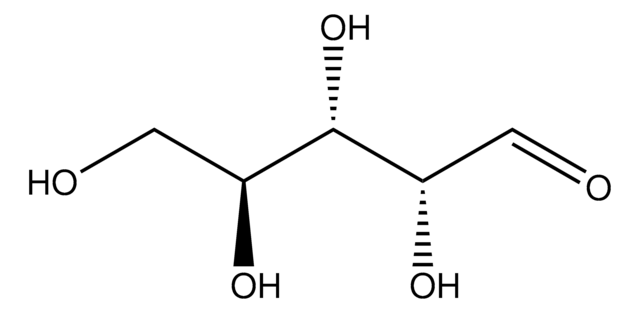
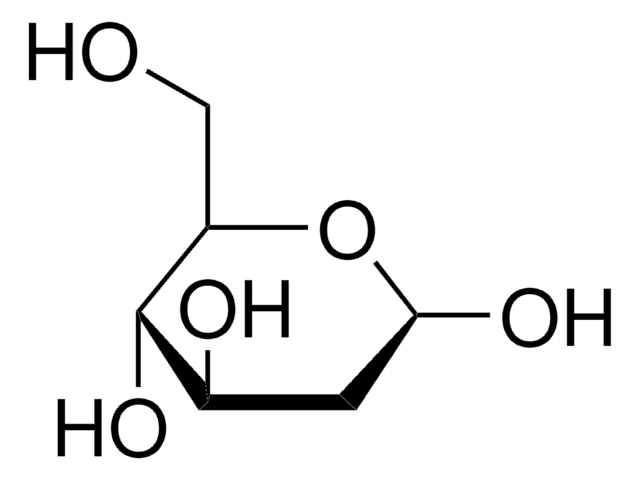
2-Deoxy-D-ribose
≥99.0% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
2-Deoxy-D-arabinose, 2-Deoxy-D-erythropentose, Thyminose
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C5H10O4
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
134.13
Beilstein:
1721978
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352201
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.0% (TLC)
form
solid
optical activity
[α]20/D −56±2°, 24 hr, c = 1% in H2O
impurities
<0.5% Sulphated ash
ign. residue
≤0.5% (as SO4)
loss
≤1% loss on drying, 20 °C (HV)
color
white
mp
89-90 °C (lit.)
solubility
water: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
2-Deoxy-D-ribose is used to study processes of oxidative stress and glycation in vivo and in vitro. 2-Deoxy-D-ribose, an endothelial-cell chemoattractant and angiogenesis-inducing factor, is used to study processes of tumor angiogenesis and progression mediated at the level of thymidine phosphorylase activity.
Other Notes
To gain a comprehensive understanding of our extensive range of Monosaccharides for your research, we encourage you to visit our Carbohydrates Category page.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Katarzyna Lamparska et al.
Nucleic acids research, 40(19), 9788-9801 (2012-08-02)
5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5azaC-dR) has been employed as an inhibitor of DNA methylation, a chemotherapeutic agent, a clastogen, a mutagen, an inducer of fragile sites and a carcinogen. However, its effects are difficult to quantify because it rapidly breaks down in aqueous
Jean Cadet et al.
Free radical research, 46(4), 367-381 (2012-01-24)
A broad scientific community is involved in investigations aimed at delineating the mechanisms of formation and cellular processing of oxidatively generated damage to nucleic acids. Perhaps as a consequence of this breadth of research expertise, there are nomenclature problems for
Marina Rossi et al.
Physical review letters, 110(10), 107801-107801 (2013-03-26)
Concentrated solutions of ultrashort duplex-forming DNA oligomers may develop various forms of liquid crystal ordering among which is the chiral nematic phase, characterized by a macroscopic helical precession of molecular orientation. The specifics of how chirality propagates from the molecular
Xican Li
Food chemistry, 141(3), 2083-2088 (2013-07-23)
The deoxyribose degradation assay is widely used to evaluate the hydroxyl (OH) radical-scavenging ability of food or medicines. We compared the hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity of 25 antioxidant samples prepared in ethanol solution with samples prepared after removing the ethanol (residue).
N S Brown et al.
The Biochemical journal, 334 ( Pt 1), 1-8 (1998-08-07)
Angiogenesis is the term used to describe the formation of new blood vessels from the existing vasculature. In order to attract new vessels, a tissue must release an endothelial-cell chemoattractant. 2-Deoxy-D-ribose is produced in vivo by the catalytic action of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service