D7145
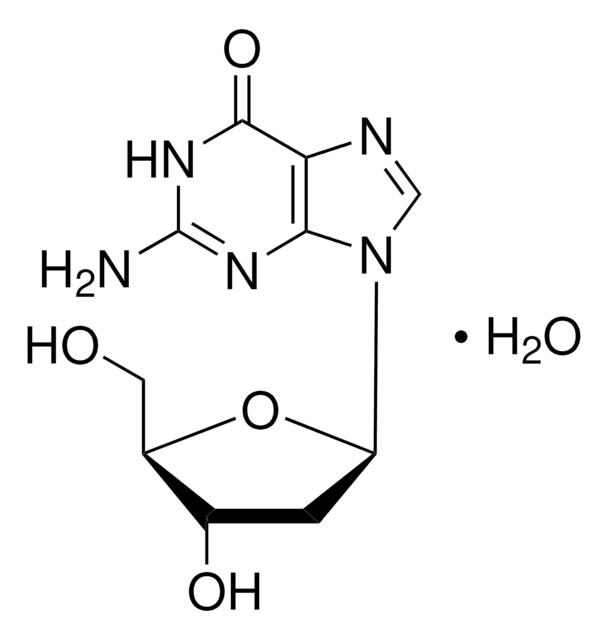
2′-Deoxyguanosine monohydrate
99-100%
동의어(들):
2′-Deoxyguanosine hydrate, 9-(2-Deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)guanine, Guanine-2′-deoxyriboside
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(5)
About This Item
실험식(Hill 표기법):
C10H13N5O4 · H2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
285.26
Beilstein:
39814
MDL number:
UNSPSC 코드:
41106305
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.51
추천 제품
생물학적 소스
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
분석
99-100%
양식
powder
solubility
1 M NH4OH: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless
SMILES string
O.NC1=Nc2c(ncn2[C@H]3C[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O3)C(=O)N1
InChI
1S/C10H13N5O4.H2O/c11-10-13-8-7(9(18)14-10)12-3-15(8)6-1-4(17)5(2-16)19-6;/h3-6,16-17H,1-2H2,(H3,11,13,14,18);1H2/t4-,5+,6+;/m0./s1
InChI key
LZSCQUCOIRGCEJ-FPKZOZHISA-N
유사한 제품을 찾으십니까? 방문 제품 비교 안내
애플리케이션
2′-Deoxyguanosine monohydrate has been used as a nucleoside supplement:
- to study its effect on mitochondrial DNA copy number in deoxyguanosine kinase (dguok) mutant zebrafish,
- in tissue culture medium for deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) synthesis,
- in RPMI (Roswell Park Memorial Institute)-1640 medium to eliminate the endogenous thymocytes
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Deoxyguanosine (dG) is a purine nucleoside that upon sequential phosphorylation (kinases) forms deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) which is used by DNA polymerases and reverse transcriptases to synthesize DNA(s). Deoxyguanosine is the most electron-rich of the four canonical bases and includes many nucleophilic sites which are susceptible to oxidative damage. This makes deoxyguanosine and its oxidized derivatives useful reagents to study mechanisms of oxidative damage to nucleosides and nucleotides.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
이미 열람한 고객
José Pedro F Angeli et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 51(2), 503-515 (2011-05-24)
Epidemiological studies have indicated that Western diets are related to an increase in a series of malignancies. Among the compounds that are credited for this toxic effect are heme and lipid peroxides. We evaluated the effects of hemoglobin (Hb) and
Sreelekha K Singh et al.
Nucleic acids research, 39(15), 6789-6801 (2011-05-17)
The oxidation of DNA resulting from reactive oxygen species generated during aerobic respiration is a major cause of genetic damage that, if not repaired, can lead to mutations and potentially an increase in the incidence of cancer and aging. A
Kasper Broedbaek et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 51(8), 1473-1479 (2011-08-09)
The increasing prevalence of diabetes together with the associated morbidity and mortality calls for additional preventive and therapeutic strategies. New biomarkers that can be used in therapy control and risk stratification as alternatives to current methods are needed and can
Takeji Takamura-Enya et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters, 21(14), 4206-4209 (2011-06-21)
BODIPY-modified 2'-deoxyguanosine was synthesized for use as a detection reagent for genotoxic compounds. BODIPY-FL is a well known fluorescence reagent whose fluorescent light emission diminishes near a guanine base by a photo-induced electron transfer process. We attached BODIPY-Fl to the
Benjamin Munro et al.
Human molecular genetics, 28(5), 796-803 (2018-11-15)
Deoxyguanosine kinase (dGK) is an essential rate-limiting component of the mitochondrial purine nucleotide salvage pathway, encoded by the nuclear gene encoding deoxyguanosine kinase (DGUOK). Mutations in DGUOK lead to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) depletion typically in the liver and brain, causing
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.