추천 제품
분석
≥98% (HPLC)
Quality Level
양식
powder
색상
white to off-white
solubility
DMSO: ≥20 mg/mL
저장 온도
room temp
SMILES string
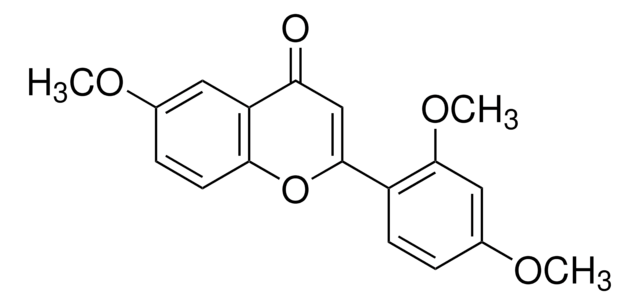
COc1ccc(cc1OC)C2=CC(=O)c3ccccc3O2
InChI
1S/C17H14O4/c1-19-15-8-7-11(9-17(15)20-2)16-10-13(18)12-5-3-4-6-14(12)21-16/h3-10H,1-2H3
InChI key
ZGHORMOOTZTQFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
관련 카테고리
애플리케이션
3′,4′-Dimethoxyflavone has been used in urease inhibition assay.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
3′,4′-Dimethoxyflavone is a flavone compound, which has the ability to prevent the production and accumulation of poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer. It guards against N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) toxicity in cortical neurons. 3′,4′-Dimethoxyflavone is a member of the class of plant-derived polyphenolic flavonoids. It is known to have antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-atherogenic, hypolipidemic and neuroprotective or neurotrophic effects.
3′,4′-dimethoxyflavone is a competitive antagonist of the AhR that inhibits AhR-mediated induction of CYP1A1, and also displays antiestrogen activity in breast tumor cell lines. The compound blocks transformation of the cytosolic AhR complex, and formation of nuclear AhR complexes.
3′,4′-dimethoxyflavone is a competitive antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) that inhibits AhR-mediated induction of CYP1A1, and also displays antiestrogen activity in breast tumor cell lines.
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
Flavonoids as natural inhibitors of jack bean urease Enzyme
AJ Awllia, et al.
Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 13(3), 243-249 (2016)
Identification through high-throughput screening of 4'-methoxyflavone and 3', 4'-dimethoxyflavone as novel neuroprotective inhibitors of parthanatos
Fatokun AA, et al.
British Journal of Pharmacology, 169(6), 1263-1278 (2013)
Nada H Eisa et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 21(21) (2020-10-30)
There is increasing evidence of the involvement of the tryptophan metabolite kynurenine (KYN) in disrupting osteogenesis and contributing to aging-related bone loss. Here, we show that KYN has an effect on bone resorption by increasing osteoclastogenesis. We have previously reported
Ke Wang et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 16(7), 16454-16468 (2015-07-25)
Exposure to aristolochic acid I (AAI) can lead to aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN), Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN) and urothelial cancer. The induction of hepatic CYP1A, especially CYP1A2, was considered to detoxify AAI so as to reduce its nephrotoxicity. We previously
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.