C8115
Coronatine
from Pseudomonas syringae pv Glycinea, >95% (HPLC)
동의어(들):
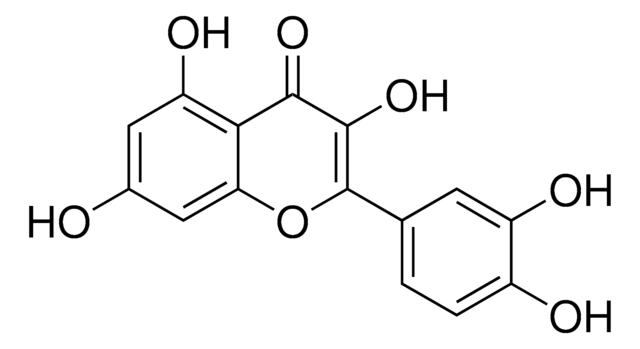
COR, Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid,2-ethyl-1-[[(6-ethyl-2,3,3a,6,7a-hexahydro-1-oxo-1H-inden-4-yl)carbonyl] amino]
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(1)
About This Item
실험식(Hill 표기법):
C18H25NO4
Molecular Weight:
319.40
MDL number:
UNSPSC 코드:
51102829
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.85
추천 제품
생물학적 소스
Pseudomonas syringae pv Glycinea
Quality Level
분석
>95% (HPLC)
양식
powder
solubility
H2O: soluble 0.2 mg/mL
DMSO: soluble 20 mg/mL
methanol: soluble 20 mg/mL
동작 모드
enzyme | interferes
저장 온도
−20°C
SMILES string
CCC1CC2C(CCC2=O)C(=C1)C(=O)NC3(CC3CC)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C18H25NO4/c1-3-10-7-13-12(5-6-15(13)20)14(8-10)16(21)19-18(17(22)23)9-11(18)4-2/h8,10-13H,3-7,9H2,1-2H3,(H,19,21)(H,22,23)
InChI key
FMGBNISRFNDECK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
애플리케이션
Coronatine is a polyketide phytotoxin produced by several members of the Pseudomonas syringae group of pathovars such as atropurpurea, glycinea, maculicola,morsprunorum and tomato. Coronatine was used to study the regulatory genes: corP, corS and corR. It was used to study the stimulation of ethylene synthesis in Nicotiana tabacum leaves.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Coronatine is a polyketide phytotoxin produced by several members of the Pseudomonas syringae group of pathovars. It consists of two distinct structural components that function as biosynthetic intermediates: coronafacic acid (CFA) and coronamic acid (CMA). It is known to induce hypertrophy and chlorosis, inhibit root elongation, and stimulate ethylene production.
Coronatine is a polyketide phytotoxin produced by several members of the Pseudomonas syringae group of pathovars. It is known to induce hypertrophy and chlorosis, inhibit root elongation, and stimulate ethylene production.
기타 정보
Keep container tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Nathalie H P Claessens et al.
The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery, 158(3), 867-877 (2019-04-16)
The aim of this study was to evaluate postoperative indices of cerebral oxygenation and autoregulation in infants with critical congenital heart disease in relation to new postoperative ischemic brain injury. This prospective, clinical cohort included 77 infants with transposition of
Essi K Ahokas et al.
Journal of strength and conditioning research, 33(6), 1488-1495 (2019-04-23)
Ahokas, EK, Ihalainen, JK, Kyröläinen, H, and Mero, AA. Effects of water immersion methods on postexercise recovery of physical and mental performance. J Strength Cond Res 33(6): 1488-1495, 2019-The aim of this study was to compare the effectiveness of 3
Román Manuel Vásquez-Elizondo et al.
Photosynthesis research, 132(3), 311-324 (2017-05-12)
The analysis of the variation of the capacity and efficiency of photosynthetic tissues to collect solar energy is fundamental to understand the differences among species in their ability to transform this energy into organic molecules. This analysis may also help
Anjelica Hodgson et al.
Histopathology, 71(2), 296-304 (2017-03-28)
TP53 mutations are characteristic of the high-grade pathway in the dual pathway of urothelial carcinogenesis. These mutations have been correlated with aberrant accumulation of p53 protein; however the definition and significance of this vary in the literature. The aim of
Shahnaj Parvin et al.
Plant, cell & environment, 41(10), 2418-2434 (2018-06-03)
Increased biomass and yield of plants grown under elevated [CO2 ] often corresponds to decreased grain N concentration ([N]), diminishing nutritional quality of crops. Legumes through their symbiotic N2 fixation may be better able to maintain biomass [N] and grain
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.