C2997
Cytosporone B
≥98% (HPLC), powder, nuclear receptor Nur77 agonist
동의어(들):
3,5-Dihydroxy-2-(1-oxooctyl)benzeneacetic acid ethyl ester, Csn-B, Csn-B; 3,5-Dihydroxy-2-(1-oxooctyl)-benzeneacetic acid, ethyl ester
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(1)
About This Item
실험식(Hill 표기법):
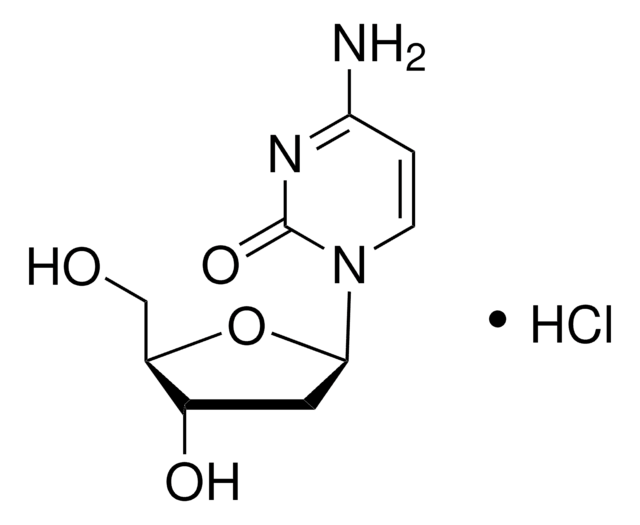
C18H26O5
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
322.40
MDL number:
UNSPSC 코드:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
추천 제품
제품명
Cytosporone B, ≥98% (HPLC)
Quality Level
분석
≥98% (HPLC)
양식
powder
색상
white to off-white
solubility
DMSO: >20 mg/mL
저장 온도
−20°C
SMILES string
CCCCCCCC(=O)c1c(O)cc(O)cc1CC(=O)OCC
InChI
1S/C18H26O5/c1-3-5-6-7-8-9-15(20)18-13(11-17(22)23-4-2)10-14(19)12-16(18)21/h10,12,19,21H,3-9,11H2,1-2H3
InChI key
UVVWQQKSNZLUQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
애플리케이션
Cytosporone B has been used:
- as a positive control and NR4A1 agonist in NR4A1 reporter gene assay
- for Nr4a1 activation
- to treat OVX mice and study its effect on migration of osteoclast precursor
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Cytosporone B (Csn-B) is the first naturally occurring agonist for nuclear orphan receptor Nur77.
Cytosporone B (Csn-B) is the first naturally occurring agonist for nuclear orphan receptor Nur77. It binds with high affinity (IC50=0.278 nM) to the ligand-binding domain of Nur77 and stimulates Nur77-dependent activities.
Nur77 is a nuclear receptor/transcription factor. A physiological ligand for Nur77 is as yet unknown, but there is increasing interest in Nur77 because of its known activities. Translocation of Nur77 from the nucleus to mitochondria initiates cell apoptosis, making it a potential target for cancer treatment. Nur77 is also involved in glucose homeostasis; it induces genes involved in gluconeogenesis. Csn-B physically binds to Nur77 and activates its transactivational activity and translocation to mitochondria to induce apoptosis. It inhibits cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Nur77 is a nuclear receptor/transcription factor. A physiological ligand for Nur77 is as yet unknown, but there is increasing interest in Nur77 because of its known activities. Translocation of Nur77 from the nucleus to mitochondria initiates cell apoptosis, making it a potential target for cancer treatment. Nur77 is also involved in glucose homeostasis; it induces genes involved in gluconeogenesis. Csn-B physically binds to Nur77 and activates its transactivational activity and translocation to mitochondria to induce apoptosis. It inhibits cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Cytosporone B is a fungal metabolite closely related to phomposin C. It is the first known agonist for the nuclear orphan receptor Nur77. It binds with high affinity (IC50 = 0.278 nM) to the ligand-binding domain of Nur77 and stimulates Nur77-dependent activities.
Nur77 is a nuclear receptor/transcription factor with no known physiological ligand, but there is increasing interest in Nur77 because of its known activities. Translocation of Nur77 from the nucleus to mitochondria initiates apoptosis, making it a potential target for cancer chemotherapy. Nur77 also induces genes involved in gluconeogenesis. Csn-B activates the Nur77 translocation to mitochondria to induce apoptosis, inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Nur77 is a nuclear receptor/transcription factor with no known physiological ligand, but there is increasing interest in Nur77 because of its known activities. Translocation of Nur77 from the nucleus to mitochondria initiates apoptosis, making it a potential target for cancer chemotherapy. Nur77 also induces genes involved in gluconeogenesis. Csn-B activates the Nur77 translocation to mitochondria to induce apoptosis, inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
신호어
Warning
유해 및 위험 성명서
예방조치 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
A C Kramer et al.
Leukemia, 31(11), 2479-2490 (2017-03-23)
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematopoietic neoplasm resulting from the malignant transformation of T-cell progenitors, and comprises ~15% and 25% of pediatric and adult ALL cases, respectively. It is well-established that activating NOTCH1 mutations are the major
Pro-angiogenic Ginsenosides F1 and Rh1 Inhibit Vascular Leakage by Modulating NR4A1
Kang JI, et al.
Scientific reports, 9(1), 4502-4502 (2019)
Aravind T Reddy et al.
PloS one, 15(2), e0229256-e0229256 (2020-02-23)
Cigarette smoke (CS) contains multiple gaseous and particulate materials that can cause lung inflammation, and smoking is the major cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). We sought to determine the mechanisms of how CS triggers lung inflammation. Nur77, a
Mohammad Ishaq et al.
Innate immunity, 26(8), 746-758 (2020-09-15)
Nuclear hormone receptor ligands are known to modulate innate immunity by dampening the immune response induced by pathogens. Here, we report that unlike other ligands, 3,3',5-triiodo-l-thyronine (T3) induced the type 1 IFN response and expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). T3
Shirley Dehn et al.
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 32(1), 254-264 (2017-09-02)
Phagocytosis after myocardial infarction (MI) is a prerequisite to cardiac repair. Recruited monocytes clear necrotic cardiomyocytes and differentiate into cardiac macrophages. Some studies have linked apoptotic cell receptors on cardiac macrophages to tissue repair; however, the contribution of precursor monocyte
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.