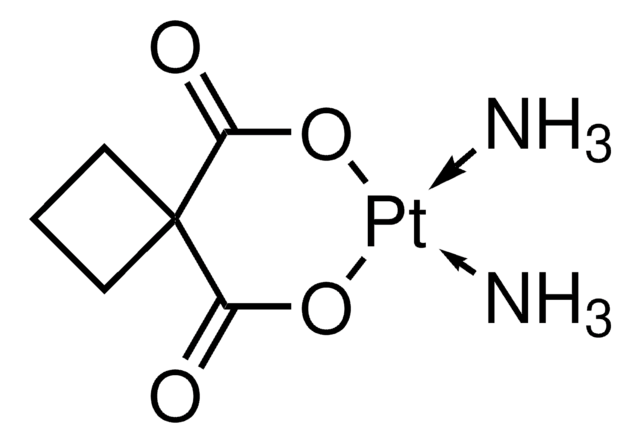
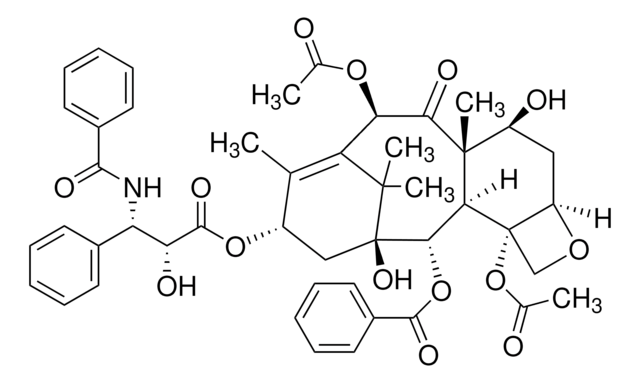
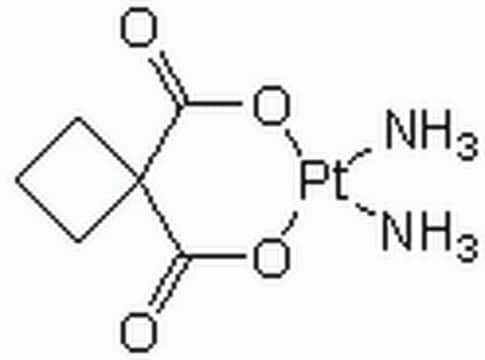
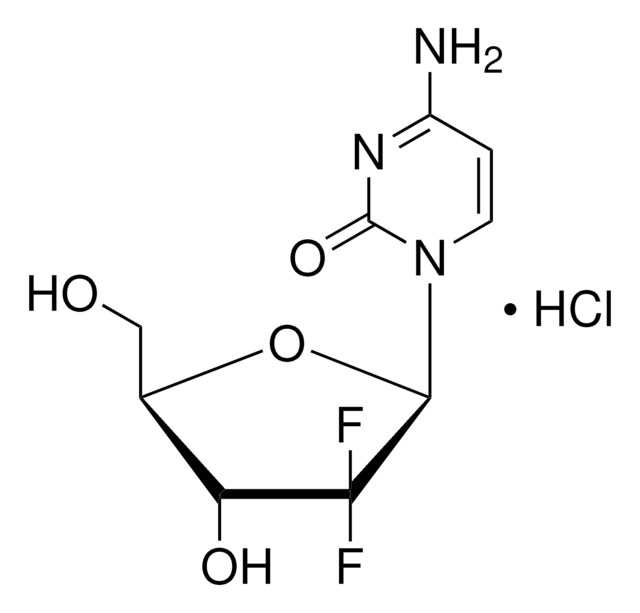
About This Item
추천 제품
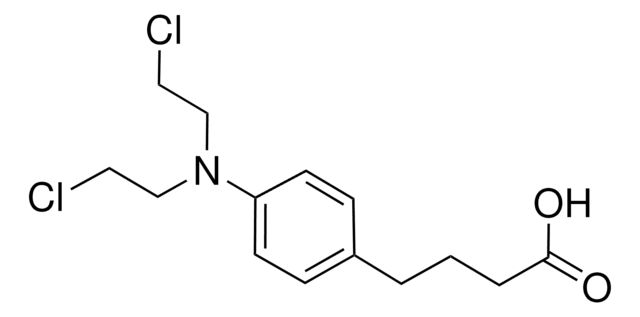
일반 설명
애플리케이션
- in chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia mouse model and treatment
- to induce cell death in a large subset of colorectal cancer cells
- in the evaluation of cell proliferation and chemosensitivity
- as a positive control for suppressed cell growth
생화학적/생리학적 작용
특징 및 장점
신호어
Danger
유해 및 위험 성명서
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Muta. 1B - Repr. 1B - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
개인 보호 장비
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
이미 열람한 고객
문서
DNA damage and repair mechanism is vital for maintaining DNA integrity. Damage to cellular DNA is involved in mutagenesis, the development of cancer among others.
관련 콘텐츠
n proliferating cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases. Gap 1 (G1) is the interval between mitosis and DNA replication that is characterized by cell growth. Replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis (S) phase, which is followed by a second gap phase (G2) during which growth and preparation for cell division occurs. Together, these three stages comprise the interphase phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is followed by the mitotic (M) phase.
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is a selective process for the removal of unnecessary, infected or transformed cells in various biological systems. As it plays a role in the homeostasis of multicellular organisms, apoptosis is tightly regulated through two principal pathways by a number of regulatory and effector molecules.
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.