L7269
α-Lactalbumin from human milk
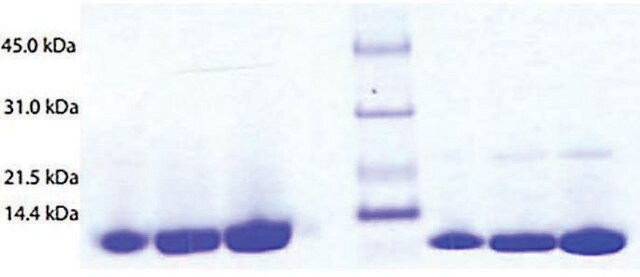
≥95% (SDS-PAGE), lyophilized powder
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human milk
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (SDS-PAGE)
form
lyophilized powder
mol wt
14,070 Da by calculation
concentration
>75 % protein (UV)
technique(s)
cell migration: suitable
solubility
H2O: soluble 10 mg/mL(lit.)
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... LALBA(3906)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
α-Lactalbumin (α-LA) is a small, acidic, whey protein that constitutes about 22% of the total proteins in human milk. It is produced by the epithelial cells of the mammary gland. α-LA is made up of two domains, a large α-helical domain, and a small β-sheet domain.
Application
α-Lactalbumin (α-LA) has been used as a standard
- to study the partitioning behavior of different monomeric proteins with exposure to amino acids on the protein surface
- to study the interaction between α-LA and cathepsin D
- to study the ability of breast milk fractions to enhance the transepithelial flux of extrinsic iron in colon carcinoma cell line
Biochem/physiol Actions
α-Lactalbumin (α-LA) forms a complex with lactose synthase within the mammary gland and plays a role in milk production and regulates milk volume. It acts as an essential source for bioactive peptides and essential amino acids such as lysine, tryptophan, branched-chain amino acids, and sulfur-containing amino acids that play a role in an infant′s nutrition. In addition, α-LA has a wide range of applications including a supplement to foster gastrointestinal health and modulate sleep and depression. α-LA also shows therapeutic effects against sarcopenia, seizures, mood disorders, and cancer. It has a Ca2+ binding site that binds with Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Mn2+ and many Zn2+ binding sites.
Alters the substrate specificity of galactosyltransferase to increase the rate of lactose formation; the complex of galactosyltransferase and α-lactalbumin is called lactose synthase.
Alters the substrate specificity of galactosyltransferase to increase the rate of lactose formation; the complex of galactosyltransferase and α-lactalbumin is called lactose synthase. Complexes of α-lactalbumin with oleic acid show drastically different activities than α-lactalbumin alone, being strongly cytotoxic to tumor cells. The complex is referred to as HAMLET (human alpha-lactalbumin made lethal to tumor cells).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Breast Milk Fractions Solubilize Fe(III) and Enhance Iron Flux across Caco-2 Cells
Robert E. S.
The Journal of Nutrition, 449?455-449?455 (2003)
Junai Gan et al.
Molecular nutrition & food research, 63(18), e1900259-e1900259 (2019-07-05)
The use of human milk products is increasing for high-risk infants. Human milk contains endogenous enzymes that comprise a dynamic proteolytic system, yet biological properties of these enzymes and their activities in response to variations including pH within infants are
Antonio Carroccio et al.
Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association, 8(3), 254-260 (2009-11-26)
A percentage of patients with symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) suffer from food hypersensitivity (FH) and improve on a food-elimination diet. No assays have satisfactory levels of sensitivity for identifying patients with FH. We evaluated the efficacy of an
Comparison of the amino acid sequence of bovine alpha-lactalbumin and hens egg white lysozyme.
K Brew et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 242(16), 3747-3749 (1967-08-25)
E A Permyakov et al.
FEBS letters, 473(3), 269-274 (2000-05-20)
Small milk protein alpha-lactalbumin (alpha-LA), a component of lactose synthase, is a simple model Ca(2+) binding protein, which does not belong to the EF-hand proteins, and a classical example of molten globule state. It has a strong Ca(2+) binding site
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service