QuinoxP*
はじめに
リン原子上に不斉中心を有する光学活性なリン配位子の中には、触媒的不斉合成において優れたエナンチオ選択性を示すものがあり1、例えばある種のP不斉配位子は、Ru及びRh触媒による水素化反応において良好もしくは優れたエナンチオ制御性を示すことが知られています2。しかし、これらの配位子は一般に空気に非常に不安定であり、取り扱いが困難であるために利用範囲が限られていました。 今本らは、電子求引性キノキサリン骨格を導入することによりこの欠点を克服し、空気に安定かつ触媒的不斉合成に有用な新規配位子QuinoxP*の開発に成功しました3。日本化学工業株式会社との提携により、Sigma-Aldrichは試験研究用のR,R-QuinoxP* を販売しています†。
QuinoxP*配位子の利点:
- 空気中、室温で容易に酸化やエピマー化を受けない
- 種々の反応において優れたエナンチオ選択性を示す
- 穏やかな条件で水素化反応が進行する
- 少ない触媒量で高いTONを実現
主な利用例:
QuinoxP*は、重要な分子変換に幅広く利用できる革新的な不斉配位子です。 以下に示すとおり、芳香族ボロン酸の触媒的不斉1,4-付加反応、エナンチオ選択的なアルキル化を伴う開環反応、不斉水素化反応など、種々の反応において高いエナンチオ選択性を発現します3。また、立体中心のリン原子が酸化されずに空気中室温で9ヶ月以上安定であることは特筆すべき点です。
Rh触媒による有用な不斉水素化反応
今本らは、不斉水素化反応のような工業的に利用価値の高い変換反応に有用な、光学的に純粋なP-キラル配位子を開発しました。 多くのプロキラルなアミノ酸やアミン類が水素化され、光学活性体が高収率で得られます(スキーム1)。 反応はメタノール中室温で3 atomという低い水素加圧条件下で進行し、 かつ、すべての水素化反応が6時間以内に終了し、96 - 99.9%eeを達成しています。 QuinoxP*類似の(S,S)-tert-Bu-BisP* 配位子4,5を用いたときと同様、1-acetylamino-1-adamantyletheneが基質の場合には劇的な立体反転が起こり、96%eeの選択性でS体が得られました(表 1)。

スキーム1
芳香族ボロン酸の不斉1,4-付加反応
Rh触媒によるエナンチオ選択的な芳香族ボロン酸のα,ß-不飽和カルボニル基への1,4-付加反応においても、QuinoxP*の高活性が見出されました3。40 - 50ºCの反応条件で高収率で付加生成物が得られています(スキーム 2)。 このRh(I)触媒システムでは、BINAPを不斉配位子として用いた場合に比べて極めて高いエナンチオ制御性を示しました6。
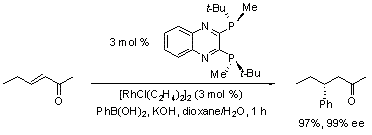
スキーム 2
Pd触媒による不斉開環反応
さらに、Pd触媒を用いるC-C結合形成反応においてもQuinoxP*の高い触媒活性が示されました。 PdCl2(cod)とQuinoxP*を室温で2時間反応させることにより、非常に高い活性の触媒が得られ、ジメチル亜鉛及びジエチル亜鉛のいずれを用いた場合にも、高いエナンチオ選択性でアルキル化を伴う開環反応が進行します(スキーム 3, 表 2)。 この触媒システムは、この種の変換反応において、これまで報告された方法の中でも、最も高い収率、高い選択性で開環生成物を与えます。 これらの結果は、上記の優れた方法論と併せて、QuinoxP* が幅広い触媒的不斉反応に有用であることを示しています。
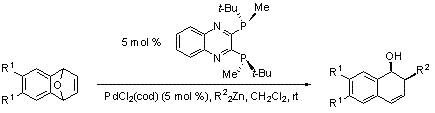
スキーム 3
製品情報
References
続きを確認するには、ログインするか、新規登録が必要です。
アカウントをお持ちではありませんか?