L0663
Anti-Laminin-2 (α-2 Chain) antibody, Rat monoclonal
clone 4H8-2, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonym(s):
Anti-Merosin
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rat
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
4H8-2, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
antigen ~400 kDa (denatured)
species reactivity
human, mouse
packaging
antibody small pack of 25 μL
General description
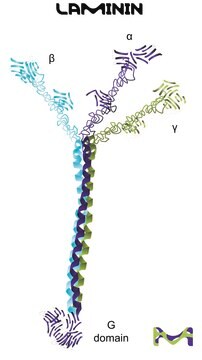
The gene LAMA2 (laminin-2) encodes a protein belonging to a large family of heterotrimeric glycoproteins called laminins. It contains a large globular C-terminal domain that binds to dystroglycan and integrin α7β1 cell receptor specific for myofibers. The amino terminal domain associates with other laminins during the formation of protein meshwork that is involved in the basal membrane supramolecular assembly. The gene is mapped to human chromosome 6q22.33.
Laminin, the most abundant structural and biologically active component in basement membrane, is a complex extracellular glycoprotein of 700-900 kDa that plays an important role in many aspects of the cell biology. It is composed of one α chain (approx. 400 kDa, previously called A chain) one β chain (215 kDa, B1) and one γ chain (205 kDa, B2), held together by disulfide bonds.
Anti-Laminin-2 (α-2 Chain) antibody, Rat monoclonal (rat IgG1 isotype) is derived from the 4H8-2 hybridoma produced by the fusion of rat myeloma cells and splenocytes from a Lewis rat immunized with mouse heart laminin-2.1 The antibody is purified from the culture supernatant of hybridoma cells grown in a bioreactor. Anti-Laminin-2 (α-2 Chain) antibody, Rat monoclonal reacts specifically with mouse1 and human2, laminin-2. The epitope recognized by the antibody resides in the N-terminal portion of the α2 chain of laminin.
Laminin, the most abundant structural and biologically active component in basement membrane, is a complex extracellular glycoprotein of 700-900 kDa that plays an important role in many aspects of the cell biology. It is composed of one α chain (approx. 400 kDa, previously called A chain) one β chain (215 kDa, B1) and one γ chain (205 kDa, B2), held together by disulfide bonds.
Anti-Laminin-2 (α-2 Chain) antibody, Rat monoclonal (rat IgG1 isotype) is derived from the 4H8-2 hybridoma produced by the fusion of rat myeloma cells and splenocytes from a Lewis rat immunized with mouse heart laminin-2.1 The antibody is purified from the culture supernatant of hybridoma cells grown in a bioreactor. Anti-Laminin-2 (α-2 Chain) antibody, Rat monoclonal reacts specifically with mouse1 and human2, laminin-2. The epitope recognized by the antibody resides in the N-terminal portion of the α2 chain of laminin.
Specificity
The epitope recognized by the antibody resides in the N-terminal portion of the α2 chain of laminin.
Immunogen
Mouse heart laminin-2
Application
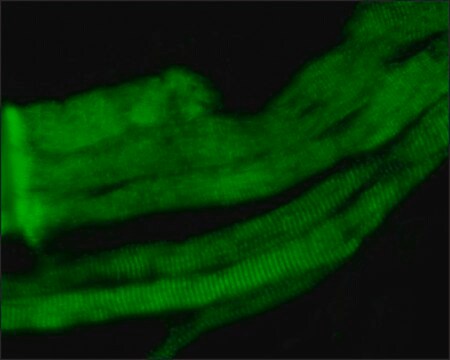
Anti-Laminin-2 (α-2 Chain) antibody, Rat monoclonal has been used in immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Laminins are glycoproteins that function in extracellular matrix architecture, cell adhesion, differentiation, and neurite outgrowth. Mutations in the gene LAMA2 (laminin-2) leading to either partial deficiency or complete absence of laminin α2 have been associated with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD), characterized by severe, early-onset congenital muscular dystrophy to mild, later childhood-onset limb-girdle type muscular dystrophy, hypotonia with muscle weakness at early infancy, poor spontaneous movements with contractures of the large joints, and weak cry along with respiratory dysfunction.
Physical form
Solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Preparation Note
Purified from the culture supernatant of hybridoma cells grown in a bioreactor.
Storage and Stability
For continuous use, store at 2-8 °C for up to one month. For extended storage, freeze in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in "frostfree" freezers, is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify the solution by centrifugation before use. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
recommended
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Jennifer D Bernet et al.
Nature medicine, 20(3), 265-271 (2014-02-18)
Skeletal muscle aging results in a gradual loss of skeletal muscle mass, skeletal muscle function and regenerative capacity, which can lead to sarcopenia and increased mortality. Although the mechanisms underlying sarcopenia remain unclear, the skeletal muscle stem cell, or satellite
The role of pericytic laminin in blood brain barrier integrity maintenance.
Gautam J, et.al.
Scientific Reports, 6, 36450-36450 (2016)
Expression and distribution of laminin a1 and a2 chains in embryonic and adult mouse tissues: an immunochemical approach.
Sasaki T, et al.
Experimental Cell Research, 275(2), 185-199 (2002)
Andrea Lh Arnett et al.
Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development, 1 (2015-01-13)
Adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors are becoming an important tool for gene therapy of numerous genetic and other disorders. Several recombinant AAV vectors (rAAV) have the ability to transduce striated muscles in a variety of animals following intramuscular and intravascular administration
Thomas C Roberts et al.
Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids, 1, e39-e39 (2013-01-25)
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small RNAs that regulate gene expression and are implicated in wide-ranging cellular processes and pathological conditions including Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). We have compared differential miRNA expression in proximal and distal limb muscles, diaphragm
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service